Why is the area of a circle pi times the square of the radius?
The
usual definition of pi is the ratio of the circumference of a
circle to
its diameter, so that the circumference of a circle is pi times
the
diameter, or 2 pi times the radius. The animation above shows that
a
circle can be divided into concentric rings which can be unrolled
to
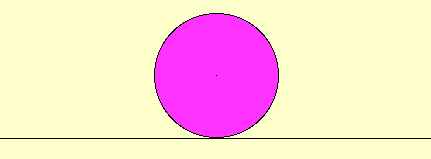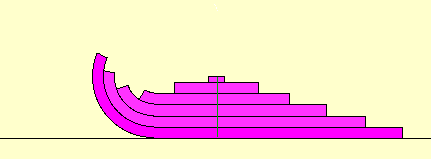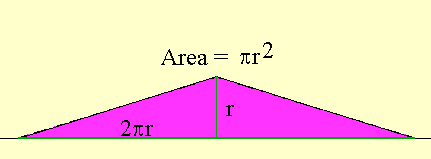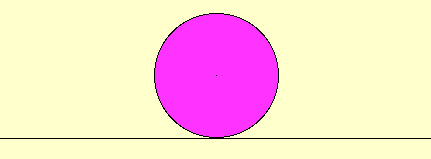
closely resemble a triangle (with height r and base 2 pi times r)
of
area pi times the square of the radius. By dividing the
circle
into more rings and unrolling, the result more closely matches a
triangle, so the approximation becomes better. Taking more
and
more rings, the triangle of area "pi r squared" approximates the
area
of the circle arbitrarily close. This gives a geometrc
justification that the area of a circle really is "pi r squared".
For another justification for the area of a circle, see The Area of a Circle.
Last updated, Jan. 29, 2008
Tom.Richmond@WKU.edu